With several temples and ghats, Ayodhya is a sacred place for people who want to have a spiritual experience. In addition to remnants of the Nawabi era, it is home to several religious sites, including the Ram Janmabhoomi Temple complex, Hanuman Garhi Temple, Kanak Bhawan Temple, and Nageshwarnath Temple. Take tips from this Ayodhya travel guide to help you explore all the places on time and make the best of your Ayodhya tourism.
How to reach Ayodhya
- By air: Maharishi Valmiki International Airport, or Ayodhya Airport, is the main airport situated around 15 km from the city centre. The airport has one terminal that caters to several flights to Ayodhya from around the country.
- By train: Ayodhya Cantt and Ayodhya Dham are the main railway stations connecting it to almost all major cities and towns.
- By bus: Private and public buses are a convenient way to reach the city. Services of Uttar Pradesh Transport Corporation buses are available 24 hours a day, and it is effortless to get here from nearby cities.
- Getting around/local transport in Ayodhya: Private cabs/cars, buses, auto-rickshaws, and cycle rickshaws are the primary modes of transportation for navigating Ayodhya's streets and bustling lanes. Auto-rickshaws are readily available and can be hailed for short to medium distances.

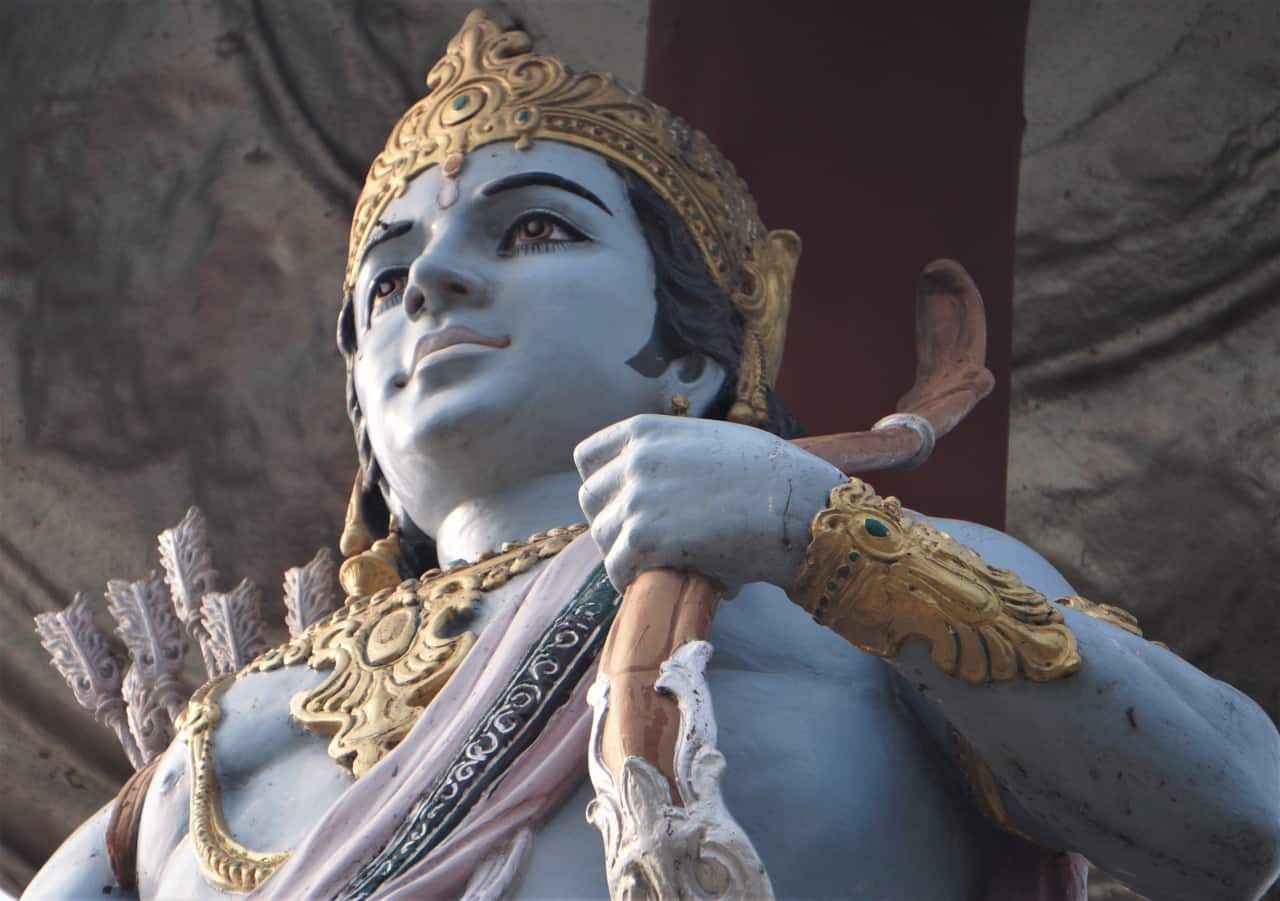
Ram Janmabhoomi Temple
A revered pilgrimage destination that is culturally and religiously significant, it is believed to be the birthplace of Lord Rama.
Exploration time: 1-2 hours%20Large.jpeg)
Hanuman Garhi
Exploration time: 1-2 hours
Kanak Bhawan
Exploration time: 1 hour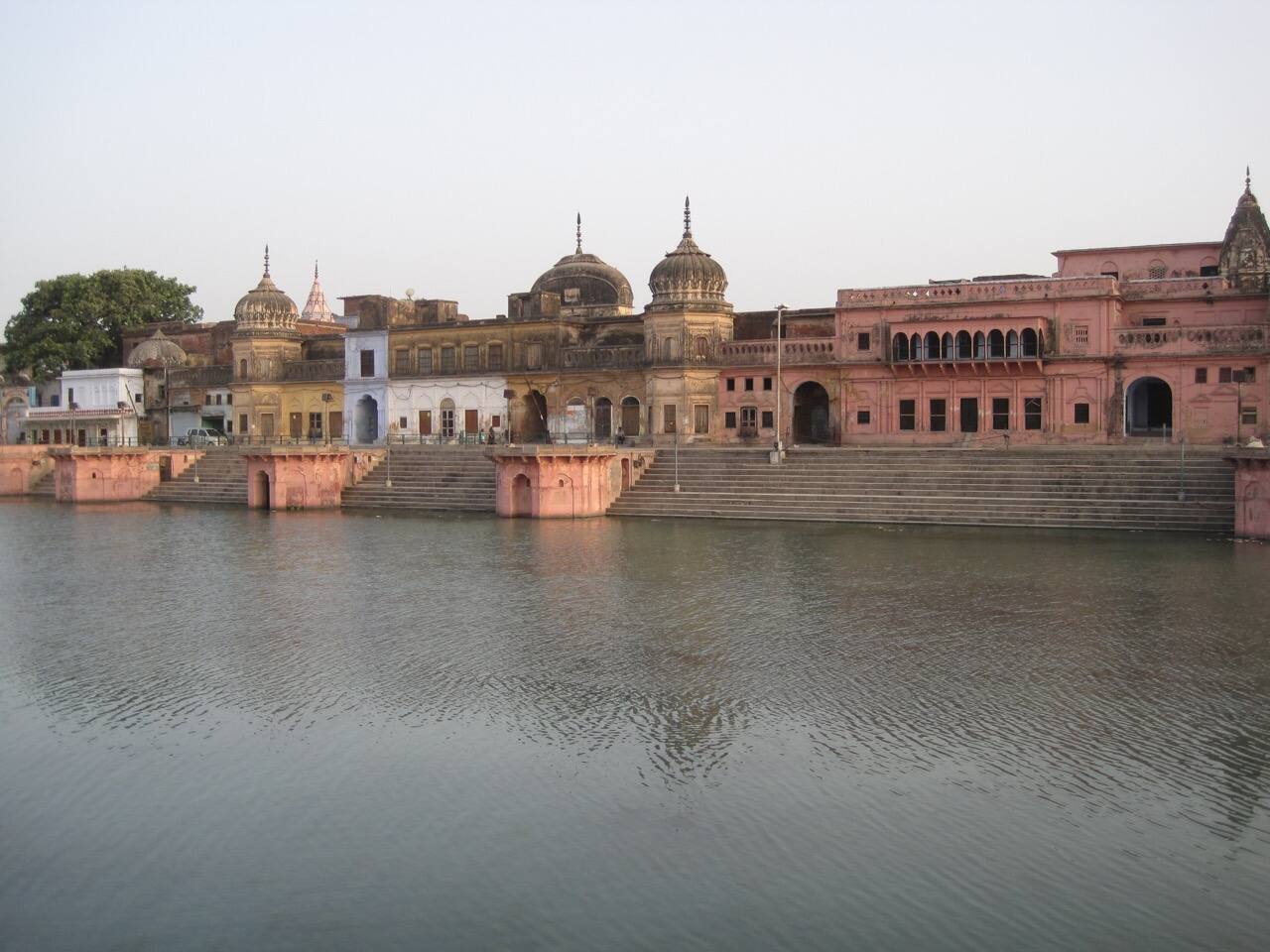
Treta Ke Thakur
Exploration time: 1 hour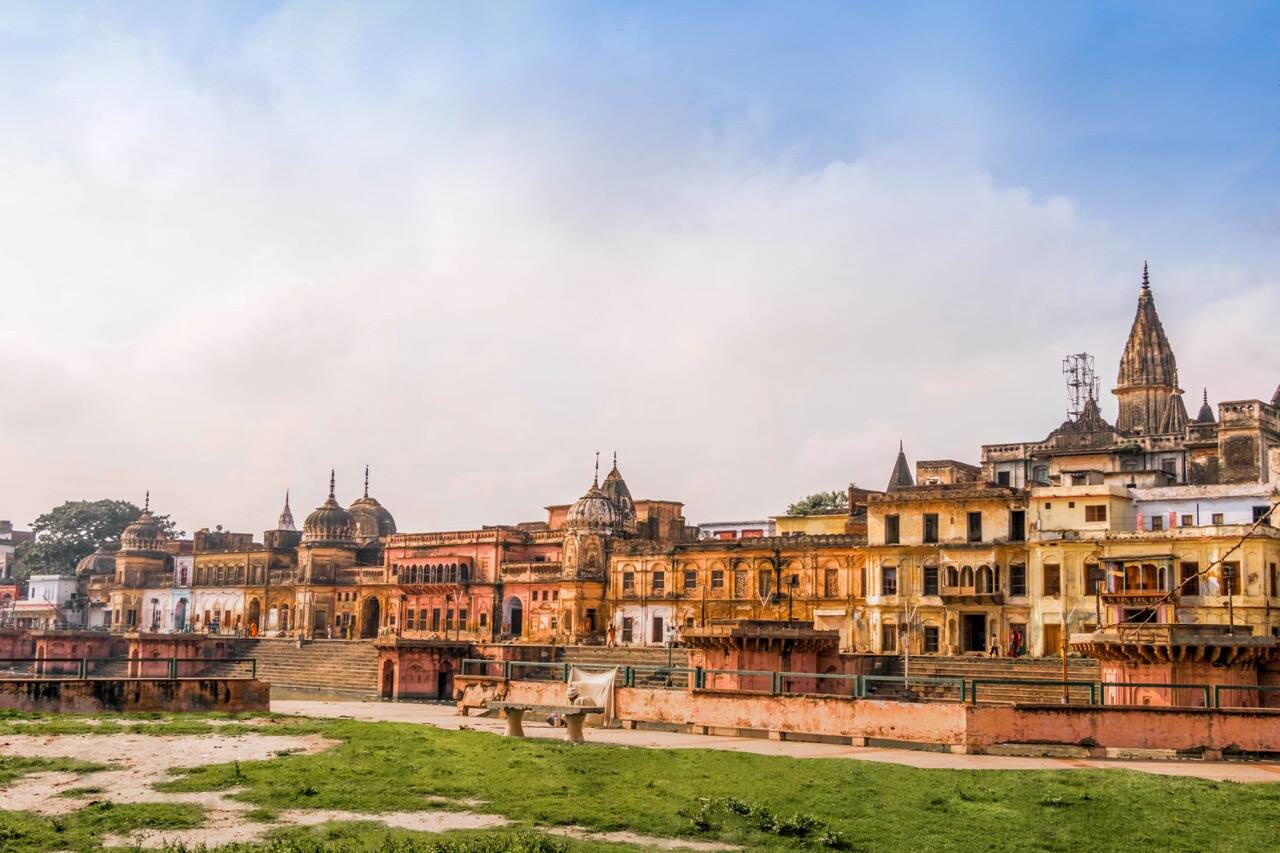
Nageshwarnath Temple
Exploration time: 1 hour
Guptar Ghat
Exploration time: 1-2 hoursPlaces to eat
Ayodhya offers various dining options catering to different tastes and preferences. Here are some popular places to eat in Ayodhya:
Things To Do
Besides being the birthplace of Lord Ram, there are many other activities one can indulge in to have the most of their experience.
Best time to visit
The most suitable time to explore Ayodhya is during the winter months, from October to March, as the weather is cool and pleasant with temperatures ranging from 15°C to 25°C
Most commonly spoken languages
Hindi and Awadhi are the most commonly spoken regional languages in Ayodhya. However, English is also widely spoken here.
While the city is primarily known for its religious and historical significance, it also offers a variety of shopping options for visitors. Some popular shopping places in Ayodhya include:
- Ayodhya Market: Ayodhya Market is famous for buying essentials for puja/prayers like idols, incense sticks, flower garlands, and diyas (oil lamps). It is also a perfect place to try street food and snacks.
- Guptar Ghat Market: Located near the Guptar Ghat, this market offers a range of items including idols, puja items, and souvenirs related to Lord Rama and the Ramayana.
- Hanuman Garhi Market: Located near the Hanuman Garhi temple, this market offers idols, pictures, and books related to Lord Hanuman.
Ayodhya is known for its high-spirited and colourful festivals which reflect the city's rich cultural and religious heritage. Some of the major festivals celebrated in Ayodhya include:
More reasons to visit
The city is steeped in history, spirituality, and cultural heritage, making it a fascinating destination to explore. Here are some more compelling reasons to visit Ayodhya:
- Valmiki Ramayan Bhawan: This museum showcases the life and teachings of Lord Rama as described in the epic Ramayana. It houses paintings, sculptures, and artefacts related to the epic.
- Naya Ghat: Naya Ghat is known for its serene and picturesque surroundings, offering a peaceful escape from the hustle and bustle of the city. The ghat is lined with steps that lead to the River Sarayu.
- Gulab Bari: Gulab Bari, also known as the Rose Garden, is a historical garden built by Nawab Shuja-ud-Daula, the third Nawab of Awadh, in the early 19th century. The garden is known for its beautiful landscaping, Mughal-style architecture, and variety of roses.
- Handicrafts and souvenirs stalls: Handicrafts and souvenir stalls showcase the skilled craftsmanship of Ayodhya's artisans, offering items such as hand-carved wooden toys, sandalwood artefacts, detailed marble pieces, and traditional Indian textiles.









%20Large.jpeg)







